Getting Started
This guide covers how you can quickly get started collecting dataset, job, and run metadata using OpenLineage. We'll show how to collect run-level metadata as OpenLineage events using Marquez as the HTTP backend, then explore lineage metadata via the Marquez UI.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have installed:
In this guide, we'll be using Marquez as the OpenLineage HTTP backend and running the HTTP server via Docker.
Run Marquez with Docker
The easiest way to get up and running with Marquez is Docker. Check out the Marquez source code and run the ./docker/up.sh script:
$ git clone git@github.com:MarquezProject/marquez.git && cd marquez
$ ./docker/up.sh
Pass the --build flag to the script to build images from source, or --tag X.Y.Z to use a tagged image.
Users on Apple silicon architecture encountering platform-related errors from Docker might need to enable emulation and customize the Docker services. Tips can be found in this guide.
The Marquez backend uses port 5432.
To view the Marquez UI and verify it's running, open http://localhost:3000.
The UI enables you to discover dependencies between jobs and the datasets they produce and consume via the lineage graph, view run-level metadata of current and previous job runs, and much more.
Collect Run-Level Metadata
Marquez, the reference implementation of the OpenLineage standard, is an LF AI & DATA incubation project to collect, aggregate, and visualize a data ecosystem’s metadata.
In this example, you will learn how to collect dataset and job metadata using the Marquez LineageAPI and UI.
When you submit a lineage event, you first need to define a unique run ID similar to 0176a8c2-fe01-7439-87e6-56a1a1b4029f. UUIDv7 format is recommended, and it should be unique. This run ID will enable the tracking of run-level metadata over time for a job that may have a name, like my-job. So, let's get started!
Step 1: Start a Run
Use the run ID 0176a8c2-fe01-7439-87e6-56a1a1b4029f to start the run for my-job with my-input as the input dataset:
REQUEST
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/api/v1/lineage \
-i -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"eventType": "START",
"eventTime": "2020-12-28T19:52:00.001+10:00",
"run": {
"runId": "0176a8c2-fe01-7439-87e6-56a1a1b4029f"
},
"job": {
"namespace": "my-namespace",
"name": "my-job"
},
"inputs": [{
"namespace": "my-namespace",
"name": "my-input"
}],
"producer": "https://github.com/OpenLineage/OpenLineage/blob/v1-0-0/client",
"schemaURL": "https://openlineage.io/spec/1-0-5/OpenLineage.json#/definitions/RunEvent"
}'
RESPONSE
201 CREATED
Step 2: Complete a Run
Use 0176a8c2-fe01-7439-87e6-56a1a1b4029f to complete the run for my-job with my-output as the output dataset. We also specify the schema facet to collect the schema for my-output before marking the run as completed. Note, you don't have to specify the input dataset my-input again for the run since it has already been associated with the run ID:
REQUEST
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/api/v1/lineage \
-i -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"eventType": "COMPLETE",
"eventTime": "2020-12-28T20:52:00.001+10:00",
"run": {
"runId": "0176a8c2-fe01-7439-87e6-56a1a1b4029f"
},
"job": {
"namespace": "my-namespace",
"name": "my-job"
},
"outputs": [{
"namespace": "my-namespace",
"name": "my-output",
"facets": {
"schema": {
"_producer": "https://github.com/OpenLineage/OpenLineage/blob/v1-0-0/client",
"_schemaURL": "https://github.com/OpenLineage/OpenLineage/blob/v1-0-0/spec/OpenLineage.json#/definitions/SchemaDatasetFacet",
"fields": [
{ "name": "a", "type": "VARCHAR"},
{ "name": "b", "type": "VARCHAR"}
]
}
}
}],
"producer": "https://github.com/OpenLineage/OpenLineage/blob/v1-0-0/client",
"schemaURL": "https://openlineage.io/spec/1-0-5/OpenLineage.json#/definitions/RunEvent"
}'
RESPONSE
201 CREATED
View Collected Lineage Metadata
Search Job Metadata
To view lineage metadata collected by Marquez, browse to the UI by visiting http://localhost:3000. Then, use the search bar in the upper right-side of the page and search for the job my-job. To view lineage metadata for my-job, click on the job from the drop-down list:
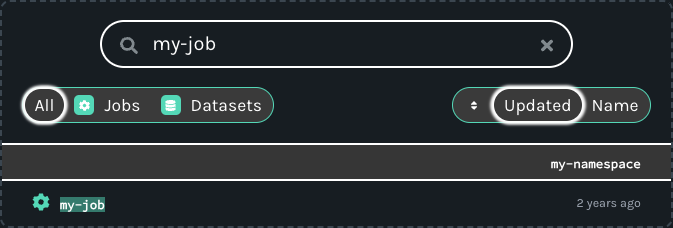
View Job Metadata
In the search result, you should see the job namespace and name, and in the lineage graph you should see my-input as an input dataset and my-output as an output dataset. In the RUN HISTORY tab on the Job Detail page below the graph, the job run state should be COMPLETED.
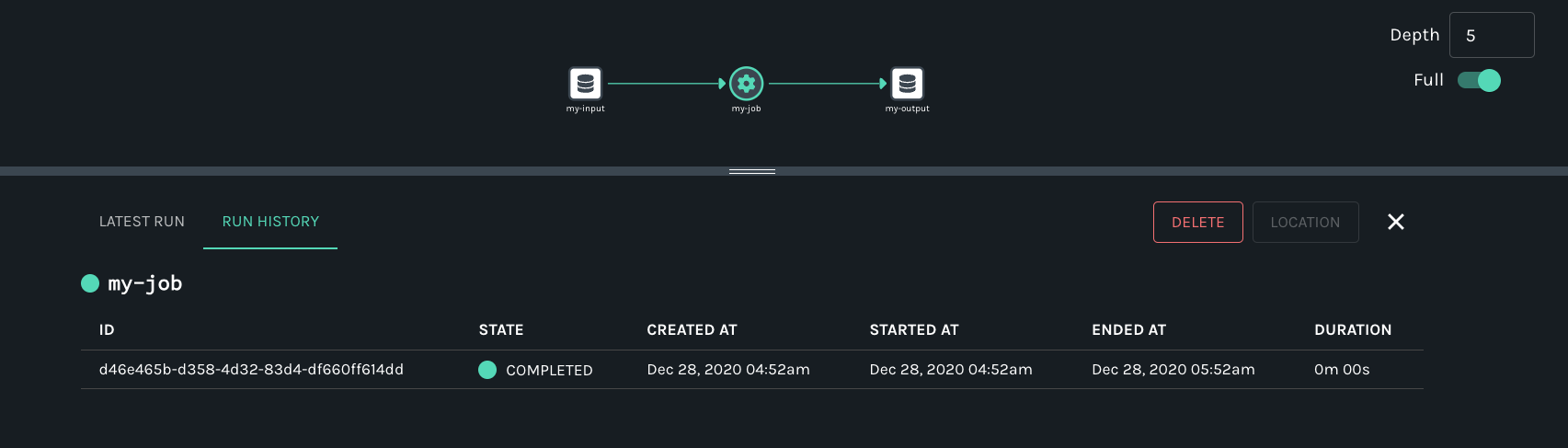
View Input Dataset Metadata
Finally, click on the output dataset my-output for my-job. Metadata displayed includes the name, column names, data types, and more:
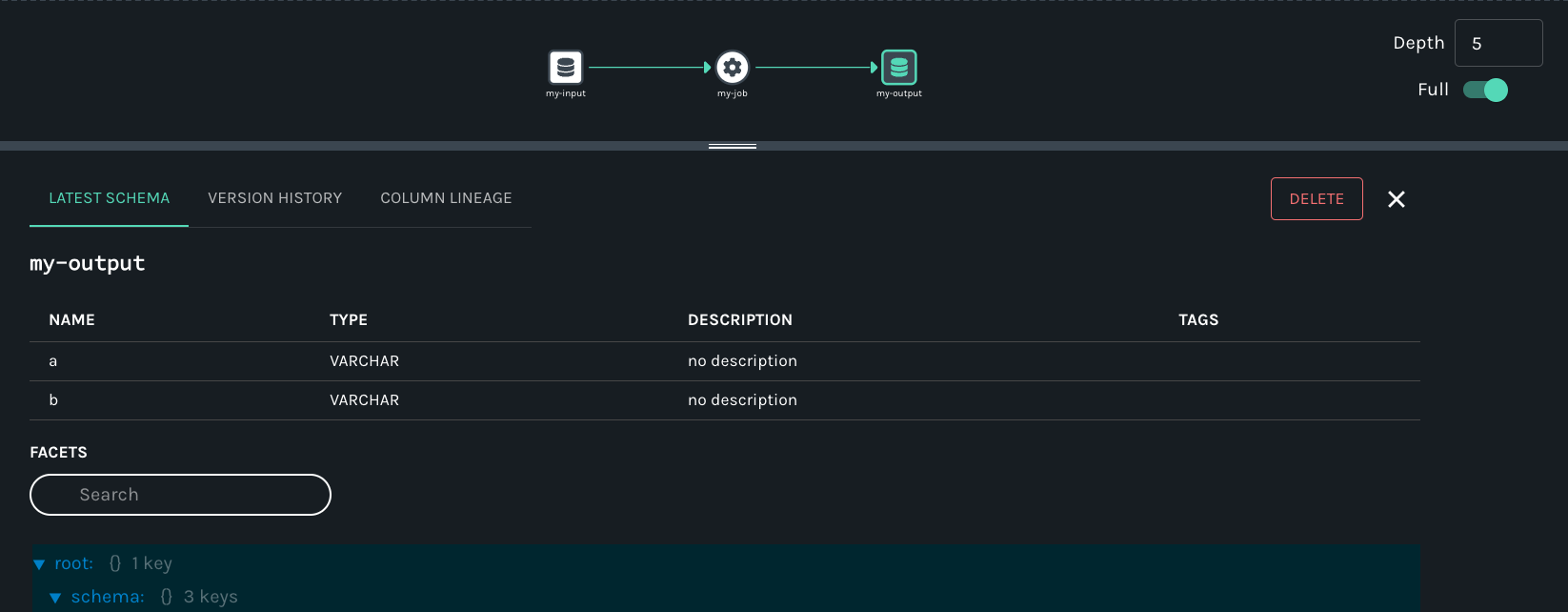
Summary
In this simple example, we showed you how to use Marquez to collect dataset and job metadata with Openlineage. We also walked you through the set of HTTP API calls to successfully mark a run as complete and view the lineage metadata collected with Marquez.
Next Steps
- Take a look at Marquez's Airflow example to learn how to enable OpenLineage metadata collection for Airflow DAGs and troubleshoot failing DAGs using Marquez.
- Watch Cross-platform Data Lineage with OpenLineage.
- Watch Column-level Lineage is Coming to the Rescue.
- Watch Observability for Data Pipelines with OpenLineage.
- Watch Data Observability and Pipelines: OpenLineage and Marquez.
- Listen to Solving Data Lineage Tracking And Data Discovery At WeWork.
- Listen to Unlocking The Power of Data Lineage In Your Platform with OpenLineage.
Feedback
What did you think of this guide? We would love to hear feedback, and we can be found on the OpenLineage Slack.